
Why Surgery?
- Do you eat less but still gain weight?
- Given your lifestyle, is it difficult to exercise?
- Is the weight loss insignificant after diet & exercise?
- Are you suffering from Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, Irregular Periods, Snoring or Joint Pains?
Bariatric surgery is the right weight loss option for you!
Endoscopic weight loss surgery results in:
- Upto 80% excess weight loss
- Sustained weight loss in most
- Resolution/improvement of associated diseases like diabetes, joint pains, sleep apnoea, raised cholesterol, high blood pressure etc.
What is bariatric surgery?

Bariatric surgery (weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Weight loss is achieved by reducing the size of the stomach with a gastric band or through removal of a portion of the stomach (sleeve gastrectomy or biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch) or by re-routing the small intestines to a small stomach pouch (gastric bypass surgery).
Studies show that the procedures cause significant long-term loss of weight, recovery from diabetes, improvement in cardiovascular risk factors, and a reduction in mortality.
The Obesity Surgery Society of India(OSSI) has recommeded that bariatric surgery can be offered to over 37.5 BMI patients even without any other disease and for people with BMI 32.5 with coexisting medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnoea, PCOD, osteo-arthritis & seriously impaired lifestyle.
International Diabetes Federation(IDF) in a position statement has recommended surgery for >27.5 BMI with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes in patients with atleast 1 cardio-vascular risk factor.
Dr Goel is also doing a clinical trial for surgical treatment of diabetes in > 23 BMI patients.
Summary of Bariatric Patient Acceptance at CMS
- 37.5 – Bariatric Surgery
- >32.5 with associated diseases – Bariatric Surgery
- >27.5 with uncontrolled T2DM with Cardio-vascular risk factor – Bariatric Surgery
- >23 with uncontrolled T2DM – Ileal Interposition(Clinical Trial)
Procedures
- Gastric Bypass
- Lap Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Mini Gastric Bypass
- Ileal Transposition
- Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion
- Laparoscopic Duodenal Switch
- Robotic Surgery
Gastric Bypass
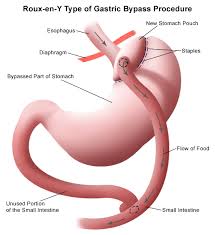
Is the oldest bariatric procedure being carried out for last 50-60 years.
Surgery involves creating a small stomach pouch & rerouting the small intestines Rest of the stomach remains functional & is connected to intestine.
The person feels full with a small portion of food and due to associated mal-absorption, part of the food is not absorbed by the body.
This surgery results in hormonal changes which lead to better control of blood sugars in diabetic patients.
Complications – Besides usual complications associated with a surgery in an obese like infection, wound dehiscence, pulmonary embolism, incisional hernia etc, specific complications include post op bleeding, leak, dumping etc. The possibility of most of these can be reduced substantially with pre-op preparation, careful technique & post-op compliance.
Co-morbidity Resolution – ~0.05% (None in our series since 2000).
Special Dietary Requirements – Post op protein requirement is 60-100 gms protein/day. Besides person is expected to consume vitamins, calcium & B12 supplements daily to avoid deficiencies.
Advantages:
- World’s most researched & accepted procedure
- Substantial long term weight loss esp. in Banded bypass
- Complete resolution of reflux & acidity symptoms
- Significant blood sugar control even in long term diabetics
Lap Sleeve Gastrectomy
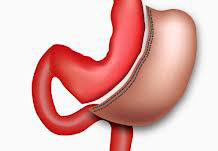 Sleeve gastrectomy is a procedure that induces weight loss by restricting food intake. The sleeve gastrectomy is an operation in which the left side of the stomach is surgically removed.
Sleeve gastrectomy is a procedure that induces weight loss by restricting food intake. The sleeve gastrectomy is an operation in which the left side of the stomach is surgically removed.
This results in a stomach, which is roughly the size and shape of a banana. Since this operation does not involve any “rerouting” or reconnecting of the intestines, it is a simpler operation than the gastric bypass or the duodenal switch.
Advantages of the Sleeve Gastrectomy:
- It does not require disconnecting or reconnecting the intestines
- It is a technically simpler operation than the gastric bypass or the duodenal switch
- It is known to reduce hunger by removal of hunger stimulating hormone producing part of stomach
- Unlike gastric bypass & gastric band, patients feels full with liquids as well
Special Dietary Requirement
Higher protein intake, multi vitamin & mineral supplementation prevents any nutritional deficiencies.
Complications
The reported incidence of complications is at par with other major surgeries performed on obese. These include – Operative Mortality – ~0.2% (None in our series since 2005).
Intra-operative Complications
~1.4% including bleeding, injury & stapler malfunctioning etc.
Early Complications
This includes wound infections, pulmonary embolism, leaks, bleeding & cardio-pulmonary complications etc.
Late Complications
These includes gall stone formation, incisional hernia, rarely intractable vomiting, ulcer, weight regain, metabolic sequelae including iron deficiency, B12, Folate deficiencies etc.
Weight Loss
The average excess weight loss is > ~70% after sleeve gastrectomy surgery.
Co-morbidity improvement
Mini Gastric Bypass
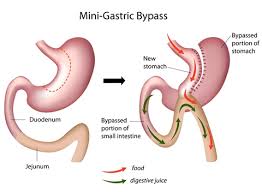 A recent procedure – combination of sleeve and bypass. Usually results in substantial weight loss even though the person is able to eat a larger meal.
A recent procedure – combination of sleeve and bypass. Usually results in substantial weight loss even though the person is able to eat a larger meal.
A long sleeve of stomach is created along with bypass of rest of the stomach and long segment of intestine.
Ileal Transposition
Ileal Transposition (surgery for thin/ normal weight diabetics)
Ileal Transposition surgery developed by Dr. Aureo de Paula from Brazil, is performed under clinical trial protocol by Dr Goel at Mumbai. It is expected to help glycemic control in selected type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Ileal Transposition
A segment of the last part of the intestine (ileum) is interposed between 2 parts of the small intestine (jejunum) just beyond stomach. No part of the small intestine is removed or bypassed.
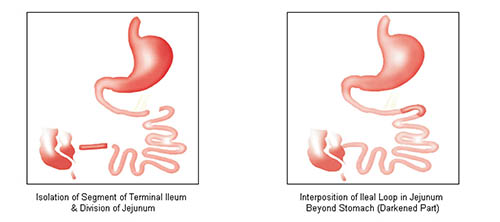
Proposed Mechanisms of Blood Sugar Control:
Blood glucose control even in patients with severe beta cell impairment. The suggested mechanisms of blood sugar control are
- Early contact of undigested food (chyle) with interposed segment of ileum results in increased blood levels of GLP-1 hormone levels. GLP-1 is supposed to have the following effect.
- Blood Glucose control even with severe beta cell impairment
- Stimulates insulin secretion
- Exerts proliferative effect on pancreatic beta cells
- This is believed to result in acute insulin response, which is usually lost in type 2 diabetes. This leads to blood sugar control immediately after a meal.
Post Op recovery:
- Immediate between 1 & 2 days
- Most of the patients are in recovery /intensive care between 1 & 2 days due to their medical limitations
- Most of the patients are allowed to have liquids after 24 hours of surgery
- Patients are encouraged to walk by evening on day of surgery
- Delayed
- Usually patients are sent home on the 5th day after surgery
- Patients can resume normal work after 2 weeks after discharge from hospital
Long term results
Ileal Transposition is based on hindgut hypothesis derived from Roux-n-y gastric bypass surgery. Long term follow up data of gastric bypass has shown 80-100% blood sugar and insulin maintenance even after 14 years
Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion
This primarily malabsorptive operation differs from the Gastric Bypass and the gastric banding, which work mainly through restriction.
The amount of excess weight loss after the BPD has been reported to be around 70 percent with weight loss in some patients persisting up to 18 years. This surgery provides the best long term weight maintenance. However being a malabsorption operation, the protein & vitamin requirement is significantly higher & requires life-long close monitoring.
Laparoscopic Duodenal Switch
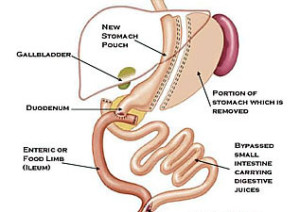 The duodenal switch (DS) is a modification of the BPD designed to prevent ulcers, increase the amount of gastric restriction, minimize the incidence of dumping syndrome, and reduce the severity of protein-calorie malnutrition. This procedure has some of the highest reported weight loss in long-term studies.
The duodenal switch (DS) is a modification of the BPD designed to prevent ulcers, increase the amount of gastric restriction, minimize the incidence of dumping syndrome, and reduce the severity of protein-calorie malnutrition. This procedure has some of the highest reported weight loss in long-term studies.
Advantages of BPD and DS:
- Increased amount of food intake compared to the bypass and band
- Less food intolerance
- Possibly greater long-term weight loss
- More rapid weight loss compared with gastric banding procedures.
Complications:
Besides other complications associated with gastric bypass, BPD-DS is also associated with
- Diarrhea and foul smelling gas, with an average of 3-4 loose bowel movements a day
- Malabsorption of fat soluble vitamins (Vitamins A, D, E and K)
Robotic Surgery
Bariatric surgery requires high dexterity & attention. Dr Goel is trained in robotic bariatric surgery at Buffalo, USA & has access to Da Vinci Si HD robot at Asian Hospital, Mumbai.
Robotic surgery reduces possibility of human error coupled with precision offered by highly evolved technology from Intuitive Surgical. Though the surgical cost increases, the quality assurance should be an important consideration.
Post Operative Bariatric Care
Individual counselling is provided by our team keeping in mind the preferences and lifestyle of the patient. The changes in eating habits required after surgery are scientifically explained so that it is easier to understand & follow. Regular monitoring helps avoid deficiencies.
LIQUID DIET (2 weeks)
- Clear liquids for first 3 days- Water,coconut water( if sugars are normal),clear soups,green tea,lime water etc. The hydration levels should be adequate.
- 4th day onwards- Protein shakes,thin dal,buttermilk,tea/coffee,soups are allowed.
SOFT DIET
Sleeve(4 weeks) & Bypass(2 weeks)
Eggwhites, fish,porridge,,dal,khichdi,low fat paneer,curd,idli,dhokla,beans etc are advised.
Foods should be soft (overcooked)
Breads,salads etc not allowed
FULL DIET
There are no restrictions except on high calorie foods with fats or sugars. Emphasis is on adequate protein intake (50-60 gms) in a day & liquids(1.5-2 litres).
Exercise
- Patient is encouraged to walk on the day of surgery
- Long walks/ slow treadmill is advised 10 days later
- Aerobic activity like swimming can begin from the 20th day
- Upper & lower body workouts can be started 1 month after surgery
- Abdominal exercises should be avoided for 3 months
Supplements
Multivitamins,Calcium,Iron & Vitamin B12 are prescribed.
Follow up Investigations
Vitamin and Mineral levels are checked every 6 months for 1 year & annually thereafter.
Support Group
Support helps and motivates post surgery patients achieve better weight loss and deal with the issues related to diet, recipes and exercise by sharing experiences and communicating with peers. Support groups meetings are an important component of a bariatric program.














